Home > Insight > IT Business
GIS for Electric Utilities: Unlocking Efficiency and Reliability
10 minutes read
Audio description available
February 5, 2025
Electric utilities are under constant pressure to improve grid reliability, optimize asset management, and enhance customer service. How can they achieve these goals in a cost-effective and sustainable manner? GIS for electric utilities provides a powerful solution.
This blog post will delve into the various ways GIS is being used by electric utilities to overcome operational challenges and achieve tangible results.

1. GIS for Electric Utility Operations
1.1. Some Common Challenges:
Electric utilities face a complex and evolving operational landscape. Some key challenges include:
- Real-time situational awareness: Utilities often struggle to obtain a comprehensive, up-to-the-minute view of their network. This lack of real-time situational awareness can lead to delayed responses to developing issues.
- Optimal site selection: Planning and constructing new infrastructure, such as substations and power lines, requires careful consideration of numerous factors. Utilities must balance technical requirements with environmental impact, land use regulations, community acceptance, and cost considerations.
- Aging infrastructure: Maintaining and upgrading aging power grids and other assets while minimizing disruption to service, especially with growing energy demands.
- Data silos and integration: Electric utilities rely on vast amounts of data from various sources, including sensors, meters, and other systems. However, this data is often siloed in different departments and systems, making it difficult to get a holistic view of operations. This lack of data integration can lead to incomplete or inaccurate information, hindering effective decision-making.
1.2. What is GIS and Why is it Relevant to the Industry?
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) provide a powerful platform for addressing these challenges. GIS is a framework for capturing, managing, analyzing, and visualizing data that has a spatial component – in other words, data that is tied to a specific location.
For electric utilities, this means being able to see, understand, and interact with information about their assets and the surrounding environment in a geographically meaningful way. By integrating location data with other relevant information (e.g., asset condition, surrounding environment), GIS for electric utilities can provide valuable insights that would be otherwise hidden. They can visualize their entire network, analyze grid performance, identify potential risks, and make more informed decisions.
1.3. Key Benefits of GIS for Electric Utilities in Operations:
GIS offers a wide range of advantages that empower electric utilities to operate more reliably and sustainably. Here are some key overarching benefits:
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: GIS streamlines workflows, automates tasks, and provides access to real-time information, leading to significant improvements in operational efficiency and cost reduction across the utility.
- Improved Decision-Making: By providing a comprehensive view of the network and its performance, GIS empowers data-driven decision-making at all levels, from strategic planning to day-to-day operations.
- Enhanced Resilience: GIS helps prevent outages, minimize downtime, and improve response to emergencies, leading to a more resilient and reliable power grid.
Now that we've outlined the key benefits of GIS for electric utilities, let's explore the specific applications that make these advantages a reality.
Learn more: Web map service provider
2. GIS for Electric Utilities: Power Grid Management
GIS transforms power grid management by providing the tools for proactive monitoring and control. Its ability to visualize geographic data enables constant vigilance and rapid response, ensuring grid stability and minimizing disruptions.
2.1. GIS aids power grid planning & design:
GIS plays a crucial role in optimizing power grid planning and design, encompassing several key areas. When planning new substations or power lines, GIS helps identify optimal locations by considering factors like proximity to existing infrastructure, land use restrictions, environmental impact, and community needs. Suitability analysis tools within GIS evaluate multiple criteria simultaneously, helping planners find the best balance between technical requirements and other considerations.
Furthermore, GIS-based network models allow engineers to simulate power flow and analyze grid performance under various scenarios, optimizing grid design and ensuring stability. This includes modeling the impact of new generation sources or changes in demand to inform grid upgrades and expansions.
Finally, GIS for electric utilities helps manage vegetation encroachment, a major cause of outages and wildfires, by leveraging high-resolution imagery and LiDAR data to identify high-risk areas and prioritize vegetation management activities.
2.2. GIS provides real-time monitoring and control:
This significantly enhances power grid management in several keyways. To begin with, interactive dashboards and visualization tools provide operators with a real-time window into grid performance, displaying key metrics such as voltage levels, current flows, and equipment status on interactive maps. This real-time visibility enables quick identification and proactive address of potential problems like voltage deviations or overloaded lines, preventing outages and improving grid stability.
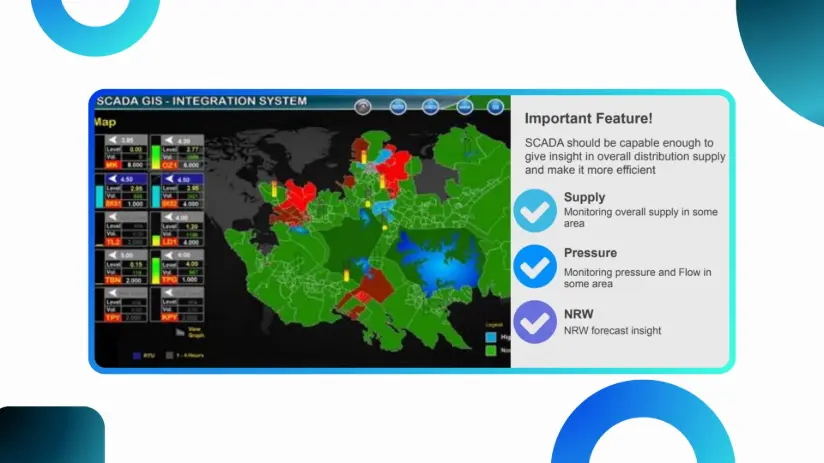
Real time control with GIS-SCADA integration
Source: LinkedIn
Furthermore, this real-time capability extends to outage management, where GIS-based outage management systems (OMS) integrate data from various sources—including smart meters, customer reports, and field crews—to pinpoint outage locations, assess impact, and dispatch repair crews efficiently. Automated customer communication features within these systems provide timely updates and estimated restoration times, minimizing disruption.
Beyond immediate response, GIS for electric utilities also facilitates predictive maintenance by integrating sensor data from grid equipment and leveraging predictive analytics. By analyzing historical performance, real-time sensor readings, and environmental factors, GIS can anticipate equipment failures, enabling proactive maintenance scheduling, minimizing downtime, and optimizing asset lifespan.
3. GIS for Electric Utilities: Asset Management
GIS provides the tools and data integration capabilities to optimize asset management throughout the lifecycle of utility infrastructure.
3.1. Infrastructure Planning:
Beyond the power grid, GIS for electric utilities provides crucial support for comprehensive infrastructure planning within electric utilities, extending itself to encompass long-term system planning and community engagement. Whether planning new transmission lines, substations, or other facilities, GIS integrates a wide range of factors to inform decisions. By incorporating demand forecasts, environmental considerations such as land use and zoning, endangered species habitats and unfavorable terrain, GIS ensures the proposed projects comply with regulations and be sustainable.
3.2. Power Grid and Utility Asset Management:
GIS for electric utilities provides a centralized platform for managing all utility assets, from large substations to individual meters. By integrating data from various sources, GIS creates a comprehensive view of each asset, including its location, condition, maintenance history, and other relevant information. This single source of truth improves data accuracy and facilitates more efficient maintenance and repair operations. Utilities can use GIS to track the performance of assets over time, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions about maintenance and replacement.
3.3. Work Order Management:
Integrating GIS with work order management systems significantly streamlines maintenance and repair processes, especially when paired with mobile GIS solutions for field crews. When a problem is identified, the system can automatically generate a work order with the affected asset's location clearly marked on a map. Field crews, equipped with mobile GIS on their tablets or smartphones, can then access this information, receive turn-by-turn directions, and update the work order status in real-time. This real-time data flow improves communication between field crews and the control center, enhancing situational awareness and enabling faster, more effective responses.
3.4. Emergency Response and Disaster Recovery:
When natural disasters or other emergencies strike, GIS becomes an indispensable tool for responding quickly and effectively.
Following an event, GIS can be used to quickly assess the extent of damage to power grids and other infrastructure. By integrating data from various sources, including aerial imagery, satellite data, and field reports, GIS creates a clear picture of the affected areas. This helps utilities prioritize repairs, allocate resources effectively, and restore service as quickly as possible.
Additionally, GIS supports the development of efficient restoration plans by providing tools for modeling different scenarios, identifying critical infrastructure, and coordinating the efforts of emergency response teams. This ensures a faster and more organized recovery process, minimizing disruption to customers and communities.
In conclusion, GIS empowers electric utilities with tools for real-time grid management and long-term asset planning. By centralizing data and enabling analysis, GIS optimizes operations, improves reliability, and drives data-driven decisions.
4. Case Studies on the Application of GIS for Electric Utilities:
4.1. Improving Power Grid Management with GIS:
Vietnam Electricity (EVN), a major state-owned power company responsible for electricity generation, transmission, and distribution across Vietnam, faces the complex challenge of managing extensive power grid infrastructure. One of its subsidiaries, Power Transmission Company No. 3 (PTC3), has effectively leveraged GIS technology to optimize its power grid operations and improve reliability. By implementing GIS mapping software, PTC3 has achieved significant improvements in several key areas.
Locating faults on power lines, a previously time-consuming process, has been significantly streamlined thanks to GIS. Operators can now quickly pinpoint fault locations, minimizing troubleshooting time and optimizing operating costs. The system's accurate distance measurement capabilities further contribute to efficiency by aiding in surveys and determining distances for maintenance work. This improved spatial awareness allows for more proactive planning and efficient resource allocation. PTC3's GIS implementation also excels at detecting lightning-strike faults. By integrating lightning data with grid maps, operators quickly pinpoint fault locations, prioritize inspections, and restore power faster.
Through its strategic application of GIS, PTC3 exemplifies how this technology empowers proactive power grid management, improves response times, and contributes to a more stable and reliable electricity supply.
4.2. On the Asset Management aspect: GIS Powers Digital Transformation of Maintenance
Many electric utilities are leveraging GIS to transform their maintenance operations and achieve significant improvements in efficiency and reliability.
One major electric utility operating in the Middle East faced significant challenges with its asset inspection and maintenance workflows. The utility relied heavily on paper-based processes, which were often hampered by harsh weather conditions, leading to damaged or illegible forms. This resulted in inaccurate data, repeat field visits, and difficulties tracking the condition of assets across a vast service territory.
To address these challenges, the utility implemented a mobile GIS solution that integrated with their existing enterprise GIS platform. The solution included customized mobile applications for field crews to collect data using digital checklists. The mobile application also provided access to real-time asset information, including location, maintenance history, and technical specifications. Furthermore, the utility integrated its GIS with a workflow automation system to streamline work order management and improve communication between field crews and the control center.
According to industry publications, this digital transformation resulted in a significant improvement in data accuracy, a reduction in repeat field visits, and more efficient maintenance operations.
This example demonstrates how mobile GIS can empower utilities operating in challenging environments to overcome data collection hurdles and optimize their maintenance workflows.
Overall, the two case studies demonstrate the transformative potential of GIS for electric utilities. They highlight how GIS solutions can streamline operations, improve decision-making, and enhance grid reliability. However, developing and implementing these solutions requires specialized expertise and resources. Many utilities, like those highlighted in the case studies, choose to outsource certain GIS services to leverage specialized skills and optimize their investments. This begs the question: which GIS services should electric utilities outsource?
5. Relevant GIS Services for Electric Utilities to Outsourcing

For many utilities, outsourcing certain GIS services becomes a strategic decision, allowing them to focus on core operations while leveraging external expertise. This approach can offer cost savings, access to cutting-edge technology, and improved scalability. So, which GIS services are prime candidates for outsourcing? Here are some key areas to consider:
1. Data Acquisition and Processing: LiDAR, imagery capture, and data processing ensures access to expertise and equipment for accurate, reliable data.
2. Advanced Spatial Analysis and Modeling: Outsourcing provides access to specialized skills for complex grid optimization and risk assessment modeling.
3. Custom Application Development: Outsourcing accelerates development of tailored GIS applications (e.g., mobile apps, dashboards) while reducing costs and accelerating project timelines.
4. Managed Services: Outsourcing database administration, system maintenance, and hosting frees internal IT and ensures platform stability.
5. Specialized Expertise: Certain GIS tasks, such as 3D modeling, drone mapping, advanced spatial statistics, or integration with specific utility systems, may require specialized expertise that is not readily available in-house. Outsourcing these tasks provides access to niche skills and ensures that projects are completed efficiently and effectively.
Our solutions on GIS for Electric Utilities
As we've seen, outsourcing specific GIS services offers electric utilities significant advantages, from access to specialized expertise to improved cost-effectiveness. Finding the right outsourcing partner, however, is crucial for successful implementation. That partner needs a proven track record and a comprehensive range of service offerings. BHSoft brings precisely this combination of experience and expertise to the table.
Our GIS solutions span the entire GIS lifecycle. We transform complex geospatial data into clear, actionable visualizations, empowering informed decision-making. Our advanced spatial analysis and resource management capabilities optimize resource allocation, support sustainable planning, and provide valuable insights for critical infrastructure projects. We also develop custom geospatial applications tailored to the unique needs of electric utilities, including mobile solutions for field crews, web dashboards for real-time grid monitoring, and sophisticated 3D models for enhanced visualization and analysis.
Furthermore, our expertise in spatial database design and integration ensures a robust and scalable foundation for your geospatial data, integrating seamlessly with other enterprise systems.


