What is WebRTC? A Deep Dive into Real-Time Web Communication
WebRTC – web real-time communication is compelling and powerful cutting edge technology. It’s plug-in free, can be used across desktop and mobile browsers and it is supported by major modern browsers. In BHSOFT new blog post, let’s together find out more about WebRTC.
What Is Real-Time Web Communication?
Real-Time Web Communication refers to technologies that enable instant, bidirectional data exchange between users directly in web browsers or web applications. This includes audio calls, video conferencing, live chat, screen sharing, and real-time data streaming—all without requiring browser plugins or third-party installations.
At the core of modern Real-Time Web Communication is WebRTC (Web Real-Time Communication), an open standard supported by all major browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. WebRTC allows peer-to-peer communication with low latency, making it a critical foundation for interactive web experiences in 2026.
History of WebRTC
The idea of WebRTC has been developed since 2009 by a group of engineers who were responsible for Google Hangouts. At that time, to connect virtually and have video conferences and communications on the web, people have used Flash. Although Flash was very popular, the Google engineers didn’t want to continue using it. They wanted to build new technology of their own.
Till 2010, Google acquired On2, a video codec company that developed the VP codec series. Google open sourced all of On2’s assets. At the same time, Google also acquired GIPS (Global IP Solutions). The reason Google acquired both On2 and GIPS is that they would like to acquire the real-time data transfer technology and started to work on a standard for WebRTC.
May 2011, Google officially released an open source project for browser-based, real-time communication between browsers. This project was named WebRTC. During this time, W3C also published its first draft for WebRTC. Since then, Google and other major players in the web-browser market have been showing great support for WebRTC. November 2017, WebRTC version 1.0 is officially an announced feature completed by W3C. WebRTC next version is still in discussion.
Why Real-Time Web Communication Matters in 2026
In 2026, user expectations for speed and interactivity are higher than ever. Businesses are no longer competing only on features—they compete on real-time experience.
Key drivers behind the growing importance of Real-Time Web Communication include:
- Remote-first work environments requiring stable video meetings and collaboration tools
- Real-time customer support embedded directly into web platforms
- Interactive SaaS products with live dashboards and notifications
- Online education and telehealth platforms demanding low latency and high reliability
- Stricter privacy and security expectations for real-time data transmission
Read more on: Top 10 Reasons Why Software Testing Is Important
How Real-Time Web Communication Works
Real-Time Web Communication is typically built using a combination of browser APIs and backend signaling mechanisms.
1. Media Capture (getUserMedia)
This API allows web applications to securely access a user’s camera, microphone, or screen—only after explicit user permission.
2. Peer Connection (RTCPeerConnection)
RTCPeerConnection establishes a direct peer-to-peer connection between browsers, minimizing latency and reducing server load.
3. Data Channels (RTCDataChannel)
RTCDataChannel enables the transmission of non-media data (text, files, game state, sensor data) with extremely low delay—ideal for real-time collaboration and multiplayer web applications.
Together, these components form the technical backbone of Real-Time Web Communication systems.
Key Benefits of Real-Time Web Communication
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Low latency communication | Near-instant audio, video, and data exchange |
| No plugins required | Works directly in modern browsers |
| Cross-platform compatibility | Desktop, mobile, and tablet support |
| End-to-end encryption | Secure media and data transmission |
| Scalable architecture | Works with P2P or server-assisted models |
These advantages make Real-Time Web Communication especially suitable for enterprise, SaaS, and consumer-facing web platforms in 2026.
Common Use Cases of Real-Time Web Communication
Real-Time Web Communication is widely adopted across industries:
- Video conferencing and virtual meetings
- Live chat and voice support for customer service
- Remote collaboration tools and screen sharing
- Multiplayer browser-based games
- Telemedicine and online consultations
- Real-time analytics dashboards and monitoring systems
Many modern platforms integrate multiple real-time features into a single web experience, reducing dependency on native apps.
Security and Privacy Considerations in 2026
Security remains a critical concern for Real-Time Web Communication, especially as data protection regulations continue to evolve globally.
Best practices in 2026 include:
- Mandatory end-to-end encryption for audio, video, and data streams
- Secure signaling servers with authentication and access control
- Explicit user consent for media access
- Compliance with international privacy standards (GDPR-aligned policies, data minimization)
Modern WebRTC implementations are designed with security as a default, not an afterthought.
Real-Time Web Communication vs Traditional Web Communication
| Traditional Web | Real-Time Web Communication |
|---|---|
| Request-response model | Continuous, bidirectional streams |
| High latency | Low latency |
| Page refresh dependent | Live updates |
| Limited interactivity | Highly interactive experiences |
This shift explains why Real-Time Web Communication is now a core requirement for high-performance web applications.
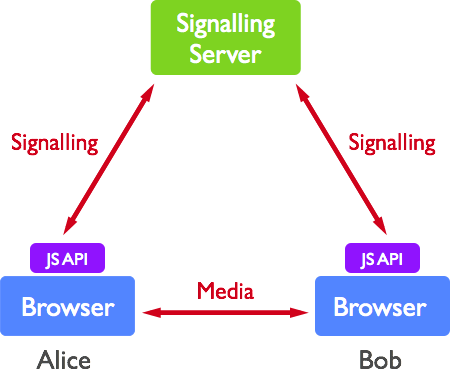
WebRTC structure
The WebRTC structure is pretty simple. It is the combination of clients connecting with each other through server signalling.
Components of WebRTC include:
getUserMedia: access user’ s camera and microphonepeerConnection: send and receive images and voice datadataChannels: send and receive other data between browsers/ applications
Future Trends of Real-Time Web Communication
Looking beyond 2026, Real-Time Web Communication continues to evolve with:
- AI-assisted noise suppression and video enhancement
- Edge computing for lower latency
- 5G and WebTransport integration
- More efficient codecs for high-resolution streaming
These advancements further strengthen the role of real-time technologies in next-generation web platforms.
Conclusion
Real-Time Web Communication has become a foundational technology for modern web applications. In 2026, it powers everything from video conferencing and customer support to collaborative SaaS platforms and interactive digital services.
By adopting Real-Time Web Communication correctly, businesses gain:
- Faster and more engaging user experiences
- Reduced dependency on native applications
- Strong security and privacy by design
- Scalable, future-ready web architectures
For any organization building interactive web solutions, Real-Time Web Communication is no longer just an enhancement—it is a necessity.
Read more: What is a virtual private network (VPN)?

