Home > Insight > Technology
React vs React Native: Decoding the Best Architecture for Your Next Project
5 minutes read
Audio description available
Jan 17, 2026
In today’s fast-paced software development landscape, choosing the right technology stack is critical to scalability, performance, and time-to-market. If you are exploring the JavaScript ecosystem, two of the most popular options you will encounter are React and React Native. While both share the same core principles—component-based architecture and declarative user interfaces—they are designed for very different purposes in the modern digital world.
As an experienced offshore software development center, BHSOFT has spent over a decade delivering complex web and mobile solutions to clients worldwide. We have seen firsthand the practical differences between a web-first approach and a mobile-first strategy. Whether you are building a data-intensive enterprise dashboard or a high-performance, cross-platform mobile application, understanding the technical distinctions between these two powerful technologies is essential to project success.
Overview of React and React Native
1. What Is React?
React (also known as ReactJS) is a JavaScript library used to build user interfaces for web applications. It was introduced by Facebook in 2011 to address the growing complexity of dynamic, data-driven user interfaces—particularly in Single Page Applications (SPAs).
At its core, React focuses on the view layer of an application. Instead of manipulating the DOM directly, developers describe how the UI should look at any given state, and React efficiently updates the browser when that state changes.
Key technical characteristics of React include:
- Component-based architecture: UI is broken down into reusable, self-contained components.
- Virtual DOM: React maintains an in-memory representation of the DOM, allowing it to batch updates and minimize expensive DOM operations.
- Declarative rendering: Developers define what the UI should look like, not how to update it step by step.
- Strong ecosystem: React integrates seamlessly with modern frontend tools such as TypeScript, Vite, Webpack, Next.js, and popular state management libraries.
Because of these features, React is widely used for:
- Data-intensive dashboards
- Enterprise web applications
- SaaS platforms
- High-interactivity user interfaces
2. What Is React Native?
React Native is an open-source framework for building cross-platform mobile applications for iOS and Android using JavaScript and React principles. It was released by Facebook in 2015 to solve a critical problem: delivering near-native mobile performance without maintaining separate codebases for each platform.
While React Native uses React’s programming model, it does not render HTML or CSS. Instead, it maps React components to native UI components provided by the underlying mobile operating system.
From a technical perspective, React Native works by:
- Running JavaScript code in a dedicated JavaScript engine (such as Hermes or JavaScriptCore)
- Communicating with native modules via a bridge or modern JSI-based architecture
- Rendering UI using real native components (e.g., UIView on iOS, View on Android)
Key strengths of React Native include:
- Code reuse across platforms: A large portion of business logic can be shared between iOS and Android.
- Native performance characteristics: UI elements are rendered using platform-native APIs.
- Access to device features: Camera, GPS, sensors, and system-level APIs via native modules.
- Familiar React development model: Hooks, state, and component patterns carry over from React.
React Native is commonly chosen for:
- Cross-platform mobile apps
- MVPs and startups targeting both iOS and Android
- Teams with strong React web experience transitioning to mobile
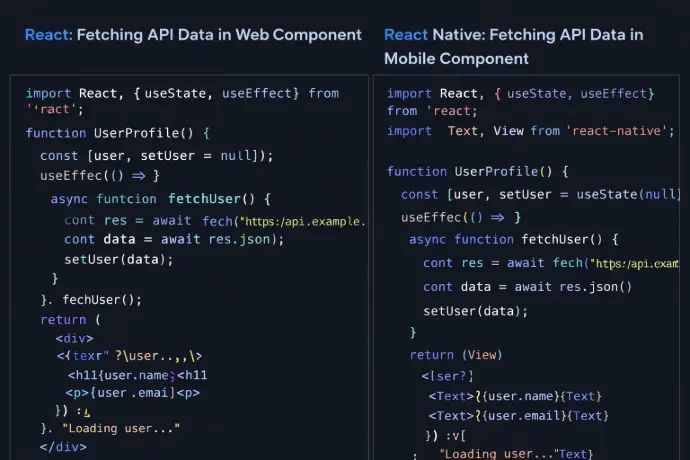
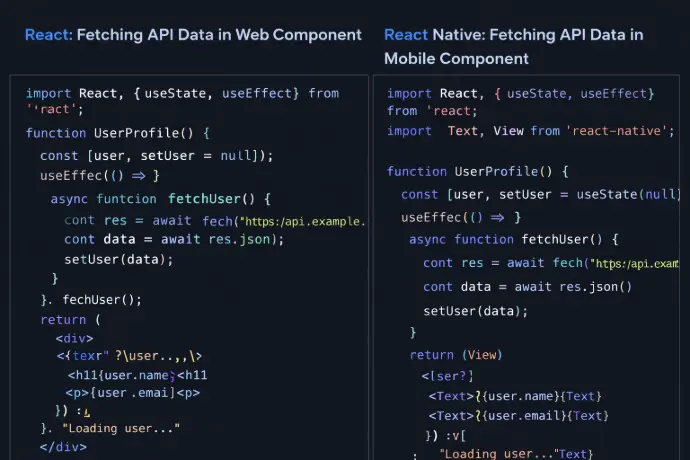
Similarities Between React and React Native
Despite targeting different platforms, React and React Native share a common development philosophy and core programming model. This shared foundation is the main reason many web developers can transition to mobile development with React Native relatively quickly. Understanding these similarities helps teams evaluate how much logic, knowledge, and architectural patterns can be reused across projects.
Shared Use of JavaScript and JSX for UI Development
Both React and React Native rely on JavaScript and JSX to describe user interfaces. JSX allows developers to write UI code that closely resembles the final structure of the application, making components easier to read, reason about, and maintain.
From a technical standpoint, this means:
- The same JavaScript language features (ES6+, async/await, modules) are used in both environments
- Component logic and UI structure follow the same mental model
- Developers familiar with React JSX syntax can quickly adapt to React Native JSX, even though the rendered output differs
Component-Based Architecture and Reusable Code Structure
Both technologies are built around a component-based architecture, where the UI is composed of small, self-contained components that manage their own state and behavior.
This approach offers several practical benefits:
- Clear separation of concerns between UI, logic, and data
- Easier code organization in large-scale applications
- High reusability of components and business logic
Consistent State Management, Hooks, and One-Way Data Flow
React and React Native both fully support Hooks, props, state, and unidirectional data flow. Concepts such as useState, useEffect, useContext, and custom hooks behave the same way in both ecosystems.
From a developer’s perspective:
- State flows downward through props
- UI updates are triggered by state changes
- Side effects are managed in a predictable lifecycle
This consistency allows teams to reuse architectural patterns, state management solutions (Redux, Zustand, React Query), and even entire custom hooks across React and React Native applications.
Reusable Business Logic and API Integration
One of the most practical similarities between React and React Native is the ability to reuse non-UI business logic. Data processing, validation, authentication flows, and API communication can often be shared with minimal changes.
Examples of reusable logic include:
- API services using fetch or axios
- Data transformation and validation layers
- Authentication and authorization logic
- State management and caching strategies
This makes it possible to adopt a shared codebase or monorepo strategy, where React handles the web UI and React Native handles the mobile UI—while both consume the same core logic.
Key Differences Between React and React Native
|
Aspect |
React (Web) |
React Native (Mobile) |
|
Primary Purpose & Platform |
Designed exclusively for web applications that run in modern browsers. React renders UI for desktop and mobile web environments using standard web technologies. |
Built for native mobile applications targeting iOS and Android, delivering a near-native user experience from a shared codebase. |
|
Library vs Framework |
React is a UI library, focused only on the view layer. Developers combine it with additional tools (routing, state management, build systems) to create a complete web stack. |
React Native is a full-fledged framework that provides core APIs, platform abstractions, and tooling required for mobile app development out of the box. |
|
UI Rendering Mechanism |
Renders UI to the HTML DOM via the browser’s rendering engine (WebKit, Blink). Performance depends on DOM updates and browser optimizations. |
Renders UI using native components such as <View>, <Text>, and <Image>, which map directly to iOS and Android UI elements. |
|
Styling Approach |
Uses standard CSS, SCSS, CSS Modules, or libraries like styled-components and Tailwind CSS for flexible styling. |
Uses StyleSheet API in JavaScript, with a CSS-like syntax but important differences (no cascading, limited selectors, Flexbox-first layout). |
|
Access to Device Features |
Limited to browser APIs. Direct access to camera, GPS, Bluetooth, or sensors requires web APIs and is often constrained by browser support. |
Provides direct access to native device APIs (camera, GPS, biometrics, sensors) through built-in or custom native modules. |
|
Development Tools & Environment |
Debugged using Chrome DevTools, React DevTools, and browser-based testing tools. Runs instantly in any modern browser. |
Requires a mobile development environment such as Android Studio, Xcode, or Expo CLI to build and run apps on simulators or physical devices. |
Pros and Cons of React vs React Native
Choosing between React and React Native requires a clear understanding of what each technology does best—and where its limitations lie.
1. React (ReactJS): Optimized for Modern Web Applications
React is widely regarded as the go-to solution for building fast, interactive, and scalable web interfaces. Its Virtual DOM architecture enables efficient UI updates, even in complex, data-heavy applications.
Pros
SEO-Friendly Performance
With support for Server-Side Rendering (SSR) and Static Site Generation (SSG) through frameworks like Next.js, React applications can be easily indexed by search engines.
Mature Ecosystem
React benefits from a rich ecosystem of tools and libraries, including state management solutions (Redux, Zustand) and routing frameworks.
Strong Developer Experience
React’s declarative approach makes UI logic predictable, easier to debug, and faster to iterate.
Cons
Platform Limitation: React is strictly for web browsers. If you need a mobile presence, you must start a separate project.
Library Fragmentation: Because React is a library, not a full framework, developers often spend extra time choosing and maintaining third-party tools for routing or form handling.
2. React Native: Cross-Platform Mobile Development
React Native enables developers to build mobile applications for both iOS and Android using a shared JavaScript codebase, while still delivering a native user experience.
Pros
High Code Reusability
A large portion of business logic can be shared across platforms, reducing development time and cost.
Native UI Performance
React Native renders real native components, resulting in smoother animations and interactions compared to web-based hybrid apps.
Fast Iteration with Hot Reloading
Developers can see UI changes instantly, significantly improving productivity during development.
Cons
Performance Overhead: For computation-heavy tasks (like advanced image processing or complex 3D rendering), React Native can lag behind pure Native (Swift/Kotlin) solutions.
Configuration Complexity: Setting up the environment (Android Studio, Xcode, CocoaPods) and managing native dependencies can be a daunting task for teams without mobile-specific expertise.
When Should You Use React or React Native?
Choosing between React and React Native depends primarily on your target platform, performance requirements, and business goals. Below are clear scenarios where each technology is the better fit.
When to Use React
React is the right choice when your product is web-first and needs to run in the browser.
Use React when you are:
- Building landing pages, Single Page Applications (SPAs), or data-heavy web dashboards
- Developing SEO-driven websites that rely on search engine visibility
- Targeting desktop and mobile web users without native device dependencies
- Integrating with modern web frameworks such as Next.js for SSR or SSG
Typical use cases include marketing websites, SaaS platforms, admin panels, and content-rich web applications.
When to Use React Native
React Native is ideal when your priority is mobile app delivery across multiple platforms.
Use React Native when you are:
- Building cross-platform mobile apps for both iOS and Android with a single codebase
- Developing an MVP that needs to reach users quickly
- Requiring access to native device features such as camera, GPS, biometrics, or push notifications
- Seeking a balance between development speed and near-native performance
Common use cases include consumer mobile apps, internal business apps, and startups validating product ideas on mobile.
Conclusion
Choosing between React and React Native ultimately comes down to your product goals and platform requirements.
At BHSOFT, we specialize in helping businesses make the right technology decisions and deliver scalable digital products. Whether you need a responsive React web application, a cross-platform React Native mobile app, or a hybrid solution that maximizes code reuse and development efficiency, our team has the expertise to bring your vision to life. From architecture consulting to full-stack implementation and ongoing support, BHSOFT ensures your project achieves performance, maintainability, and long-term success.


